Many new parents don't know what and how their children will learn when they enter kindergarten, or they may have heard some teachers or the media talk about the six literacies and learning areas, but they don't really know what they're actually talking about.
In fact, Taiwan's previous education and childcare services for preschool children were divided into kindergartens, which focused on early childhood education, and nurseries, which focused on childcare. After the integration of early childhood care in the "Early Childhood Education and Care Act," kindergartens and nurseries were merged to form "kindergartens". In order to avoid disparities in the quality of early childhood education, the Ministry of Education launched the Nursery School Education and Protection Framework in the hope that all childcare facilities in the country will have more consistent goals and curricula, and the goal of this article is to provide parents with a quick overview of the current goals of early childhood education in our country and the way in which it is taught.
Six Core Nutrients
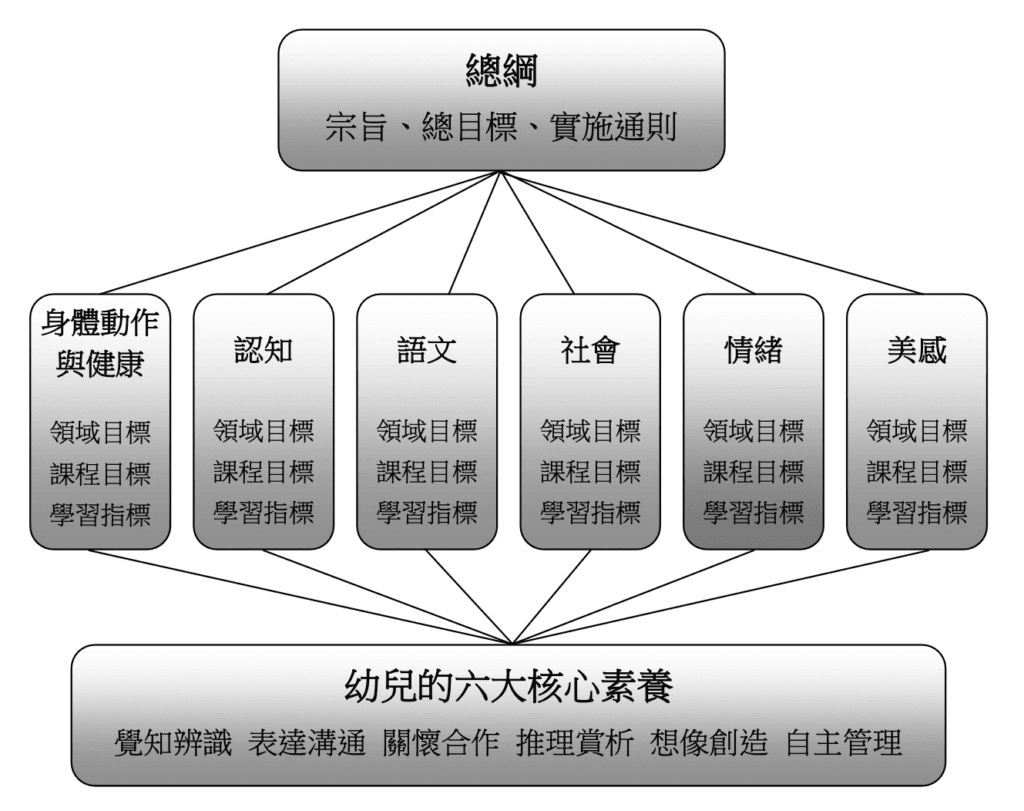
According to the Curriculum Framework for Nursery Education and Care Activities issued by the Ministry of Education, the objectives of the education and care activities are "Child-centeredThe development of the core qualities of young children.
"Core Competencies" refer to the knowledge, abilities and attitudes that a person should possess in order to adapt to the present life and to face the challenges of the future.
The Institute hopes to provide comprehensive training through the six domains."The Six Core Nutrients for Young ChildrenBelow:
- Awareness Recognition: The use of the senses to recognize messages about oneself and one's environment, and to understand the messages and their relationship to one another.
- Expressive Communication: Use a variety of symbols to express personal feelings, and listen to and share different opinions and messages.
- Caring Collaboration: A willingness to care for and accept oneself, others, the environment, and the culture, and a willingness to consult with others to build consensus and solve problems.
- Reasoned Appreciation: Use old experiences and established knowledge to analyze, integrate, and predict information, and to appreciate your own and others' performance with enjoyment.
- Imaginative Creation: Creative spirit and diverse ways of expressing feelings about people and things in the living environment.
- Self-management: Being aware of and adjusting one's actions according to norms.
What are child-centered curriculum activities?
In traditional teaching, we often see children sitting quietly in a classroom, listening to a teacher. For example, in a lesson on plants, the teacher might provide a bunch of plant-related photos and posters, place a few plants in the classroom, and teach the children about the types and characteristics of plants.
However, in child-centered education and care programs, teachers provide a variety of hands-on activities and games that allow children to learn through sensory experiences.Therefore, in a lesson about plants, teachers will take children to the schoolyard or the community to observe with their eyes, touch with their hands, smell with their noses, and even taste with their mouths the plants in the environment around them, so that they can understand what plants are through these practical experiences.

Why do I need a Kindergarten Curriculum?
"In the past, there was no syllabus and kindergartens taught children in the same way, so why do we need a syllabus now?" This is a question shared by many parents and education and child care providers. Before the integration of kindergartens, kindergartens and child care centers each followed different statutory standards for teaching and protecting activities. However, with the push for integration, the implementation of early childhood education should be standardized. At the same time, as times change, children's learning styles should also evolve with the times. Therefore, the development of curriculum frameworks is not only to ensure the quality of education for children, but also to ensure that the learning outcomes of the early years become the cornerstone of lifelong learning, so that every child has the opportunity to receive a high quality education.
Six Domains and Learning Targets
In order to emphasize the "whole person" development in early childhood, theMinistry of EducationEducational and Protective ActivitiesNon-discrimination in Academic SubjectsInstead, the six core qualities of young children are cultivated through the planning and practice of the curriculum in each area, and the curriculum outline of kindergarten teaching and care activities planned according to this concept is divided into six major learning areas.
Since its establishment 50 years ago, Jen-Ho has been practicing these six Key Learning Areas (KLAs) in daily early childhood education, such as Physical Fitness for Young Children (PFC), which focuses on the Physical Activity and Health Area (PACE):500 Examples of Physical Games for ToddlersThe "social domain", in which children are trained to interact with each other, has long been integrated into Renhe's program.PhilosophyPlease click on the links to the six areas below to see a record of the activities in the park that are mirrored by each area.
- Body Movement and Health::Enhance your toddler's physical health and fitness through play and exercise, including:
- "Awareness and Imitation"
- "Coordination and Control
- "Combination and Creation
- Recognition::Foster independent thinking processes for children to solve problems they face in life, including:
- "Gathering Information"
- "Organizing Messages"
- "Solving Problems"
- language: To help young children learn effective, appropriate, and enjoyable ways to participate in social communication systems, including:
- "Understanding."
- "Expression"
- Social::Allow toddlers to feel connected to themselves, others, and their environment, including:
- "Exploration and Awareness"
- "Negotiation and Adjustment
- "Love and Respect".
- emotion: To assist young children in developing skills related to emotional processing, including:
- "Awareness and Recognition"
- "Expression"
- "Understanding."
- "Adjustment"
- aesthetics: To help young children interact with the outside world through their senses to acquire and accumulate aesthetic experiences, including:
- "Exploration and Awareness"
- "Expression and Creation
- "Response and Appreciation
Relationship between the Six Literacies and the Six Domains of Early Childhood Care and Education Programs
How are the Early Childhood Care Activity Curriculum Areas different from the elementary schools?
Are there specific teaching objectives for the Early Childhood Curriculum Area?
Early Childhood Development Review
Many parents ask, "Is my child developmentally delayed? If you have questions about your child's development, you can start by reviewing ourOnline Preschooler Developmental ChecklistGet a quick, free checkup and then seek further professional help.
This article is referenced from the Department of Education'sCurriculum Framework for Nursery Education and Care ActivitiesThe articles published by the "Nursery" and "Education Unit" have been condensed and rewritten to make it easier for parents to understand the curriculum of the Nursery's educational and care activities.