"Influenza" is characterized by sudden onset of high fever, headache, body aches, fatigue and inflammation of the respiratory tract, cough and sore throat. Preventive measures: Drink plenty of water, rest, rinse your nose when you come back from outside, pay attention to ventilation, exercise and eat foods rich in vitamins.
"Diarrhea" - caused by rotavirus, highly contagious.
Preventive measures: Pay attention to food hygiene in the family, sterilize tableware, and take children to snacks and meals in small stalls as little as possible during the period of intestinal infectious diseases. In addition, raw fruits and vegetables should be washed and cleaned, and children should wash their hands frequently and not suck their fingers. Don't touch children during diarrhea epidemics, and don't go to places where people gather. Keep your child hydrated with fluids and electrolytes, and do not use antibiotics.
"Acute laryngitis" - the laryngeal cavity of young children is narrow, and when there is inflammation in the throat, spasmodic edema of the larynx may easily occur, which may lead to laryngeal obstruction and death by asphyxiation if not resuscitated in time. Preventive measures: Children with colds should be treated in time to avoid triggering acute laryngitis. If you find that your child's voice is hoarse, do not take it lightly, and go to the ear, nose and throat department of the hospital as soon as possible.
"Acute otitis media" - when the nose becomes more runny and the throat is inflamed after a child has a fire or a cold, bacteria or viruses in the nasopharynx can easily invade the middle ear through the Eustachian tube, causing acute suppurative otitis media. Preventive measures: Don't let water enter the ear when taking a bath, and when there is an increase in nasal discharge, you should press one nostril and blow gently, and then switch to the other side. If you have acute otitis media, don't use ear drops on your child, go to the hospital and ask an ENT doctor for treatment.
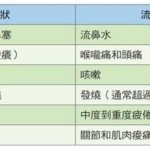
"Hand, foot and mouth (HFMD) is a common infectious disease in children caused by a variety of enteroviruses. Symptoms of fever, macules and herpes (redness around the rash) on palms and feet, herpes and/or ulcers on the mucous membranes of the mouth, and significant pain may appear first. Some patients may have cough, runny nose, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting and headache.
"Chickenpox" - After the chickenpox virus infects the human body, after an incubation period of about 2 weeks, the patient may have headache, general malaise, fever, loss of appetite and other pre-symptoms, followed by the appearance of characteristic reddish blotchy rashes, which then become papules and develop into cold sores, often accompanied by itching, and then begin to dry up and form scabs in 1-2 days, which last for about a week and then fall off. The rash is most common on the trunk, followed by the head and face, less common on the extremities, and even less common on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
"Herpes simplex pharyngitis is a disease caused by an enterovirus. Symptoms: The incubation period is 3 to 10 days. It starts with a sudden onset of high fever, which peaks at 39-41℃ in 24-48 hours, accompanied by headache, pharyngeal discomfort, myalgia, etc. Infants and children often have vomiting, refusal to eat, or even convulsions with high fever; severe sore throat, dysphagia, myalgia of the limbs, anorexia, etc. are common in older children and adults. The ulcer heals in 1 to 5 days, and the fever usually subsides within 3 days and the symptoms disappear. The prognosis of this disease is good.
"Epidemic encephalomyelitis" - an acute respiratory infectious disease caused by the bacterium Meningococcus meningitidis, initially manifested as an upper respiratory tract infection, most patients have no obvious symptoms, then the patient has sudden chills, high fever up to 40℃, headache, vomiting and recurrent episodes of headache, bleeding or bruises can be seen on the skin at an early stage, and it develops into meningitis within 1-2 days, with a high fever that does not subside, severe headache, frequent vomiting accompanied with convulsions, and even coma. Even coma occurs. Preventive measures: Immunization is the main preventive measure for children aged 1-15 years old.